
50+ Infertility Statistics
Discover 50+ essential infertility statistics and get valuable insights into this prevalent issue.
Influenza, also called the flu, is one of the most contagious and infectious diseases that affect a large number of Americans every year. An influenza epidemic can potentially disrupt society and cause high levels of absenteeism and productivity losses.
Today, when the healthcare system is overwhelmed by the coronavirus pandemic, getting a flu vaccine is more important than ever.
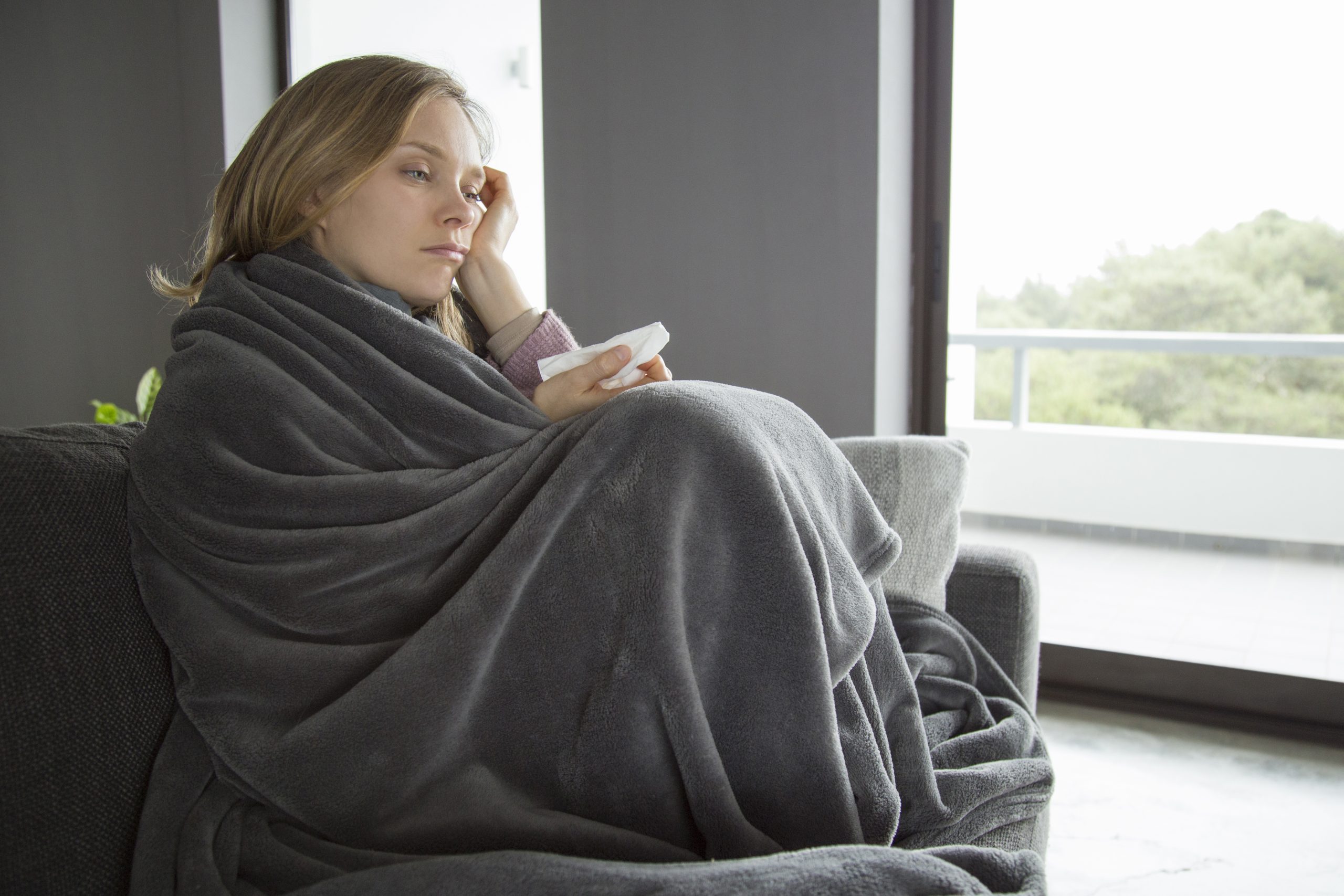


The seasonal flu is a global health threat that can be tackled swiftly and effectively by vaccinating most of the population against influenza, especially those high-risk groups of people.
Vaccinations help build herd immunity, slow the flu, and protect vulnerable groups.
Browse our curated list of vendors to find the best solution for your needs.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest trends, expert tips, and workplace insights!

Discover 50+ essential infertility statistics and get valuable insights into this prevalent issue.

As a new generation of anti-obesity drugs like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro can potentially improve millions of Americans’ health and lives, the question arises: what’s the hidden cost?

Affecting billions, work-related musculoskeletal disorders are a major health concern. Understanding how and why they happen is the first line of defense in the workplace.

Explore 30+ statistics on work, stress, and the impact of COVID-19, providing valuable insights into the challenges employees face in today’s dynamic work environment.
Shortlister Connect is a tool specifically designed to be utilized by the HR and Procurement/Sourcing teams within mid-size, large and jumbo employers. Shortlister Connect allows these teams to efficiently research & identify their optimal vendor partners, track existing vendor relationships & performance and “connect” with other employers to share successes and vendor experiences.
If you are not on the HR or Procurement/Sourcing team within an employer with over 200 employees, you will not be granted access to Connect. Examples of individuals that would not be granted access include, but are not limited to: vendors, students, practitioners, researchers, other non-employers or anyone that is unwilling to identify themselves will not pass our vetting criteria. If you are a consultant, Shortlister offers a specialized product for consultants, called Shortlister Select. You can email Tom Ciccotti at tciccotti@myshortlister.com to learn more about Shortlister Select.
***Shortlister retains the exclusive right to grant or deny access to any party to ensure the privacy of the vendors in our system.
Please login with your LinkedIn Credentials
Used by most of the top employee benefits consultants in the US, Shortlister is where you can find, research and select HR and benefits vendors for your clients.
Shortlister helps you reach your ideal prospects. Claim your free account to control your message and receive employer, consultant and health plan leads.