
What Is Payroll Software?
Explore the ins and outs of running payroll and the different methods and payroll services businesses use to compensate their employees.

Everything about running payroll starts with gross pay.
Gross wages are what attract employees, so understanding the meaning is beneficial for both workers and employers. This article will define gross and net pay, show examples of calculating gross wages for hourly and salaried workers, and determine required deductions.
Gross pay is the amount an employee earns in a specific time period before any taxes and deductions are withheld from their paycheck.
Gross wages depend on the employment status (full-time versus part-time) and wage rate (salary versus hourly) set by the employer. Gross wages for salaried employees are equal to their annual salary. For hourly employees, gross wages are calculated by multiplying the total hours worked by their hourly wage rate.

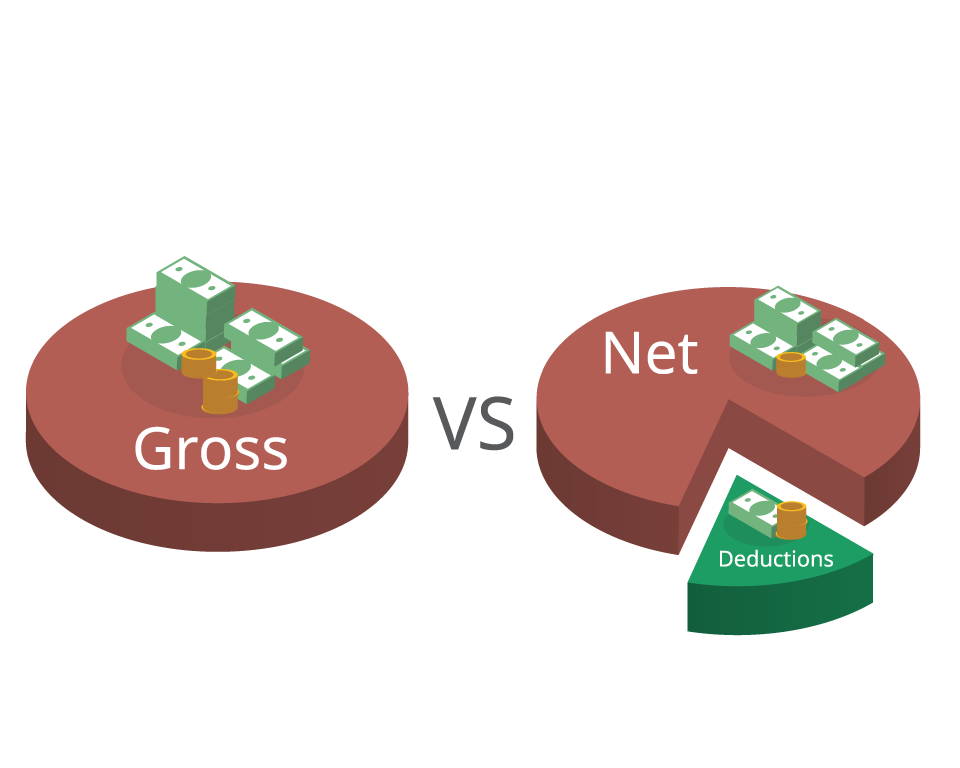
Workers will find two different numbers on their employment pay stub: gross pay and net pay.
The gross pay is considered the “top line,” and the actual take-home net pay is lower due to the deductions. Net pay is the amount of money the employee actually receives – or, in other words, the amount that appears in their bank account.
Payroll deductions include federal, state, and local income tax. Non-tax deductions include health insurance premiums, garnishments, and IRA contributions.
Gross wages can be calculated differently based on the pay period.
Employees can calculate gross pay annually, quarterly, monthly, daily, or for any other period. Calculating an employee’s gross income will depend on whether they receive hourly wages or a salary.
For hourly employees, gross wages can be calculated by simple multiplication. The number of hours worked is multiplied by the employee’s hourly wage.
For example, an employee working 25 hours per week part-time and earning $10 per hour would have a gross weekly pay of $250.
Any overtime the employee works must also be calculated as their gross wages. The overtime calculation may vary from state to state. In the U.S., most overtime pay is calculated as time and a half. Assuming the employee from the example above worked an additional 4 hours as overtime, it would be calculated as:
This means the overtime pay is $60 and needs to be added to the previously calculated gross pay. All additional sources of income, like tips, bonuses, and commissions, need to be added to the equation.
For the example above, the total pay, including overtime, equals $310.
The starting point for salaried workers is their annual salary.
To determine the gross wages per month, the employee’s yearly salary is divided by 12. Since salaried employees usually do not earn overtime, there is no need to make further calculations.
For example, an employee with an annual salary of $55,000 has a monthly gross wage of $4,583.

Since unemployment benefits partially replace lost wages due to being laid off, they are considered gross wages. This means unemployment benefits are also taxable, and the calculation varies based on the state. However, there are many calculators available online to give a rough estimate.
For example, in Maryland, employee A earned $100,000 last year ($25,000 per quarter) and has two dependents. After being laid off, he is eligible for 26 weeks of unemployment benefits at an amount of $430 per week.
Employees can view their gross wages and any deductions on their pay stubs. Gross earnings are usually the largest recorded number.
“Box 1” on the W2 form shows total taxable wages, tips, prizes, and other compensation, as well as any taxable fringe benefits. Gross wages may differ from those shown on an employee’s W2 form.
This is because some of the pre-tax deductions are not considered taxable income. Some examples of deductions that affect taxable wages:
As mentioned above, gross pay includes all of an employee’s earnings before deductions have been removed. Gross wages typically include hourly wages, salaries, or tips.

As mentioned in Shortlister’s statistics article, one in four employees agree that the most desired employer benefit is a financial wellness program with access to unbiased counselors.
Employers and employees need to have a solid grasp of the financial basics to make better-informed decisions.
Understanding an employee’s gross pay is essential because deductions and taxes are generally calculated based on the gross amount. Calculating mandatory deductions, such as the proportion in federal and state income taxes and FICA payroll withholdings, is necessary for the employer, employee, and the IRS.
If an employee pays less than required or their withholding is under-withheld, the missing amount will need to be paid over the months ahead. If an employee pays more than is required or is over-withheld, they may request a refund right away or file it in their yearly taxes.
Either way, it is crucial to correct these mistakes promptly.
An employee’s net income will always be less than their gross income. This is due to the mandatory and voluntary deductions the employers have to withhold from their salary. Finding out the employee’s gross wages is needed for other deductions based on the gross pay. These deductions are often a percentage of the gross pay.
To start off, pre-tax deductions, such as health insurance or retirement contributions, are calculated first. As the name suggests, these deductions are made from the gross pay before withholding taxes. Pre-tax deductions can be a fixed amount, such as $50 subtracted from each paycheck. In other cases, these deductions might be a percentage of the gross pay.
After pre-tax deductions, the next step is to withhold employee taxes. Taxes are often a percentage or a fixed amount of an employee’s gross wages minus pre-tax deductions. An employee’s gross wages are also used to calculate employer taxes.
After taxes, other deductions must be withheld. They can be subtracted from gross wages after taxes, and pre-tax deductions have been made. These post-tax deductions are similar to pre-tax deductions, as they can be a fixed amount or a percentage.
Calculating gross wages is simple and easy to determine. Understanding the different calculations for gross wages is essential for both employers and employees.
Browse our curated list of vendors to find the best solution for your needs.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest trends, expert tips, and workplace insights!

Explore the ins and outs of running payroll and the different methods and payroll services businesses use to compensate their employees.

While the federal minimum wage sparks a debate about whether or not it needs to be increased, one thing is certain – business owners must stay up-to-date with the latest labor law changes.

Explore the concept of imputed income, its tax implications, and the importance of accurate reporting to understand how employers handle imputed income on pay stubs and tax forms.

Explore the purpose and significance of a 147c letter, understand what it is, and when you should request one.
Used by most of the top employee benefits consultants in the US, Shortlister is where you can find, research and select HR and benefits vendors for your clients.
Shortlister helps you reach your ideal prospects. Claim your free account to control your message and receive employer, consultant and health plan leads.