
50+ Employee Financial Wellness Statistics
Uncover 50+ key statistics on employee financial wellness, providing valuable insights into the financial state within the workplace.

Insurance in the U.S. is a trillion-dollar business, making up 12.5% of the total GDP.
Seeing how insurance can be a great safeguard from the unpredictability of everyday life, especially in times of such economic uncertainty, its high demand comes as no surprise.
For individuals and families, in the case of an unexpected injury, death, property damage, or another type of loss, owning personal insurance usually cushions the financial blow and mitigates the monetary risks.
However, since there are many types of personal liability insurance policies, picking the right one requires an in-depth understanding of the product, its implementation, and overall costs.
So, what is personal insurance?
Personal liability insurance, or just personal insurance, is any type of financial coverage plan by contract that alleviates the economic burden after the loss or damage to a property, an injury, or death.
To manage risks, the insurance holder, or an insured, pays a premium fee to the insurance company or the insurer. In return, the company covers the expenses caused by the potential loss. Depending on the contract, the premiums and the amount varies.
Insurance can protect individuals or families and is often an excellent way to cover expenses that people can’t pay immediately on their own.
And although it works on the same principle, personal insurance should not be confused with commercial lines insurance since the latter primarily offers coverage for property and casualty expenses for businesses.

In the event of property damage or loss, an injury or death, personal insurance should serve as financial aid, sealed by a legally binding contract.
The insurance holder can purchase a plan that covers various liabilities, individual or for a household, and then settle on the fee.
Higher premiums usually mean better insurance coverage.
Thus, if the individual suffers a loss covered within the contract they made with the insurance agent, the compensation will largely depend on several criteria, including the premiums, the type of insurance policy, the insured’s age, and location.
There are several distinctions between personal vs. commercial lines insurance, but the main one is the liabilities they cover.
A personal insurance policy mainly covers individual losses, vehicle damage, and household insurance.
As such, it’s a popular choice that accounts for almost half of the net premiums written in the property and casualty insurance market, or 49.8%.
On the other hand, commercial insurance is aimed at small to large businesses and other enterprises and accounts for the remaining 50.2% of net premiums written. It includes everything from commercial property insurance and medical malpractice to commercial auto or casualty insurance.
Other significant differentiations between these two are:
A named insured is the person who takes out a personal insurance policy.
In the case of personal insurance, it’s an individual or a married couple. In contrast, for commercial insurance, depending on the ownership structure it, can be a variety of entities, ranging from a sole proprietor to an entire corporation.
With personal insurance, property and liability concerns cover only the loss of personal lines customers, usually with single properties and their contents. Company insurance can have much broader coverage, including various building types, offices, operations, products, employees, etc.
Unlike personal lines insurance, which has many similarities in the contracts and named insureds, a commercial policy can be significantly different from one entity to another, depending on the insured’s specific needs.
Personal liability insurance financially covers damages or injuries caused by and to the named insured and sometimes others, like close household relatives.
Depending on the insurance policy, these are the most common personal liability insurance examples:
Although this is standard coverage, the policyholder must check with their insurance agent as to what extent the policy covers all the above, especially with dog bites, since the contract might limit the insurance to certain breeds.
Although it helps in managing many financial risks, there are still some things that personal liability insurance won’t cover.
These are some of the personal liability examples that agents won’t include in the insurance policies:
Based on the needs and financial means of the named insureds, there are several types of personal insurance, including life, disability, health, and home insurance.
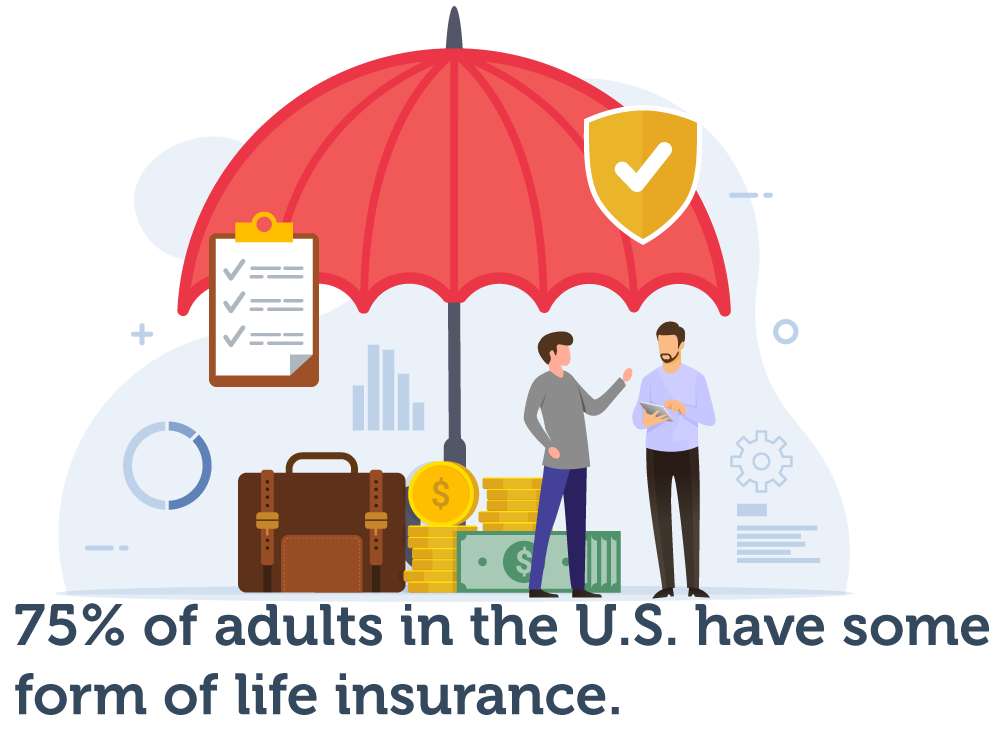
A Forbes Advisor survey reveals that at least 75% of adults in the U.S. have some form of life insurance, their reasoning being they consider it a practical means of protecting their families from unpaid debt.
The insured pays premiums to the insurance company over time as an individual or as part of a group life insurance policy, usually through an employer or civic organization.
This fee amount depends on whether they have dependents or their financial priorities, for example, leaving an inheritance that could cover college tuition, retirement, or household expenses.
In the event of an unexpected death of the insured, the insurer pays a lump sum amount to the beneficiary.
As for the types of life insurance, the main two are:
This type is permanent and has an investment or saving component.
It means that if the insured pays the premiums, the insurance is in effect, and the individual can borrow from the accumulated money.
These are time-limited and, as a result, are the more affordable option.
So, if the insured passes away while the policy is in effect, the beneficiary will get compensation. However, if the person lives past the specified time, the insurance company is not obliged to pay a benefit or refund the money.
Disability insurance falls under the personal insurance category, covering injuries or illnesses that can prevent the insurance holder from working and obtaining an income. Instead, the insurance covers a part of it.
These policies can be either short-term or long-term:
The insured can obtain them individually through disability insurance companies or their employer. When the company covers it, it can either offer a short-term policy, a long-term one, or both.
Insurance statistics reveal that by 2026, the global health insurance industry will grow to $1.2 trillion. However, according to a report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, millions of Americans do not have health insurance, or 5% of children and 13.9% of working adults.
Still, it’s not just about getting one.
Before picking the most suitable policy, the insured must know the different types of health insurance, what they mean, and the many ways to obtain them.
Health insurance can help people pay their medical bills, and sometimes it also finances a part of the cost of prescription drugs.
Usually, the insured and the insurer agree to each pay a part of the medical expenses. The amount depends on the health care coverage plan and whether it covers benefits like specialists, dental insurance, home care or nursing home care, types of medication, etc.
Getting health care insurance coverage is possible through:
Before deciding, it’s also essential to consider the deductibles and co-payments, which represent the money the insurer pays when they receive a medical service or buy prescription drugs.
As for the types of health insurance plans, they fall into three main categories, including:
Property insurance, as the name suggests, covers any damage made to the insured’s home and the things they own, including furniture, electronics, clothing, etc.
However, this broad category includes homeowners, condo, and renters’ insurance policies.
Another one that falls within this category is property damage liability coverage, which offers financial aid in case of damage done to other people’s belongings and property.
Based on the policy, there are two types of reimbursements:
There’s also the umbrella insurance option for those who want to mitigate risks and avoid losing all their savings by adding extra liability coverage.
Although it doesn’t necessarily fall under the same category as the others, personal umbrella insurance is what covers liabilities when regular auto insurance or homeowners, condo, and renters’ policies won’t.
This type of personal liability insurance covers the policyholder and their family members or people within their household.
Some examples of what personal umbrella insurance covers are:

The overall cost of personal liability insurance largely depends on the policyholder’s financial means and requirements.
Thus, the more money they invest in their premiums, the bigger the liability coverage is.
With personal insurance, the overall cost is always different.
For a working adult at the age of 40, the average cost of health insurance per month is $477, or around $6,000 per year.
According to Bankrate, on average, homeowners’ insurance will cost the policy owner $1,383 per year for a contract with $250,000 in dwelling coverage, although the price varies in each state.
For life insurance, the average for August 2023 amounts to $26 per month for applicants at the age of 40 who are purchasing a 20-year, $500,000 term life policy. Again, the cost significantly changes when insurers weigh the policyholder’s age and policy types.
As for disability insurance, usually, the policy cost varies between 1 to 3 percent of the insured’s annual salary.
Finally, the average cost for umbrella insurance is somewhat more affordable, or between $150 and $350 per year, for the first $1 million of coverage. The actual cost depends on the location of the insured and the property they own and are insuring.
A report by KPMG on the future of personal lines insurance explores the main drivers of change that could create a competitive opportunity for insurance companies, despite the ongoing economic uncertainty.
Namely, one of the main signals of change is this financial uncertainty, followed by technological advancements, customer expectations, competitive disruptions, ESG prioritization, and future regulations.
Based on these signals and insurance trends, the report demonstrates three personal insurance models that are most likely to dominate the market in the future:
Understanding what personal insurance or personal liability insurance is, together with its types and features, is a good step in the right direction when it comes to protecting people and their families from losses they couldn’t afford to cover on their own.
Regardless of the potential future transformations within this high-growth industry, personal insurance is what people turn to when they want a financial safeguard for themselves and their loved ones. And as long as there’s a mutual benefit and value, this is unlikely to change.
Browse our curated list of vendors to find the best solution for your needs.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest trends, expert tips, and workplace insights!

Uncover 50+ key statistics on employee financial wellness, providing valuable insights into the financial state within the workplace.

What if your biggest tax lever isn’t a deduction but your legal structure?

Uncover how buyers make purchasing decisions in the vast pool of alternatives and explore the ever-changing buyer’s journey.

Where should one start when building financial literacy? Discover key strategies and tools to take control of your finances and secure a brighter financial future.
Used by most of the top employee benefits consultants in the US, Shortlister is where you can find, research and select HR and benefits vendors for your clients.
Shortlister helps you reach your ideal prospects. Claim your free account to control your message and receive employer, consultant and health plan leads.